Comparing fractions is a key competency for pupils to develop in their mathematical studies. This involves understanding that fractions are a way of expressing parts of a whole. The numerator of a fraction signifies the number of parts, while the denominator represents the total number of parts in the whole.
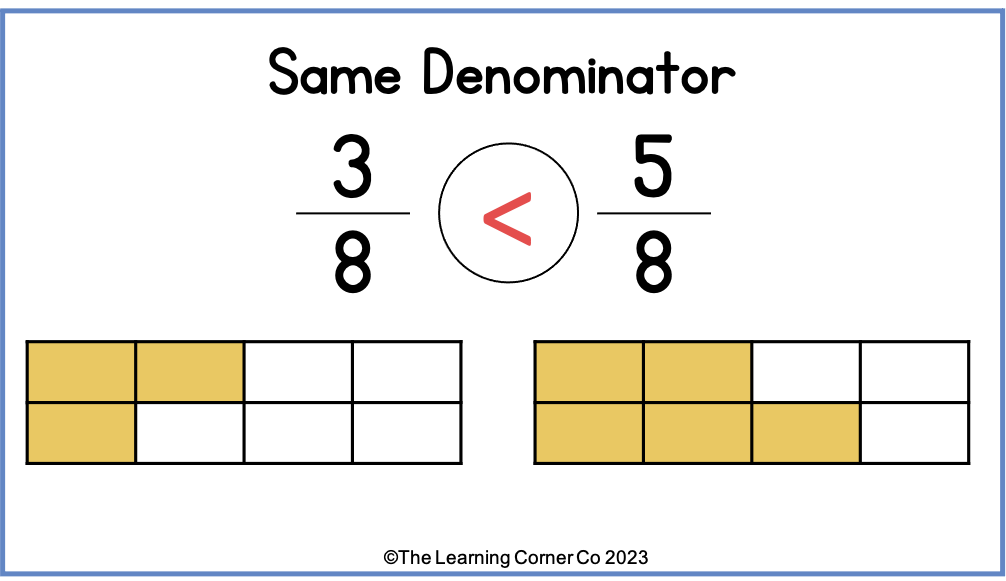
When comparing fractions with the same denominator, students need to simply evaluate the numerators. Whichever numerator is greater signifies the greater fraction. For instance, if we have the fractions 3/8 and 5/8, we can see that 5/8 is greater than 3/8 due to the larger numerator.
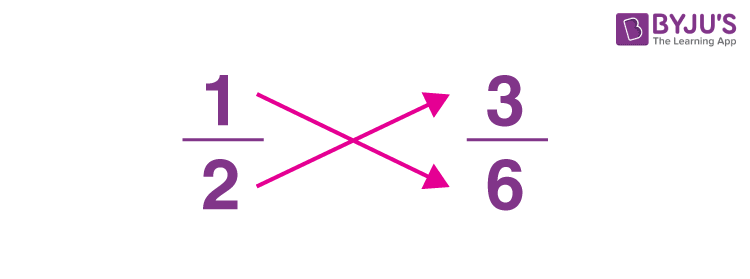
Comparing fractions with distinct denominators can be a little more tricky, but can be done by obtaining a common denominator. This can be achieved by finding the least common multiple of the two denominators. After obtaining a common denominator, they can convert the fractions to equivalent fractions with the same denominator and compare the numerators.
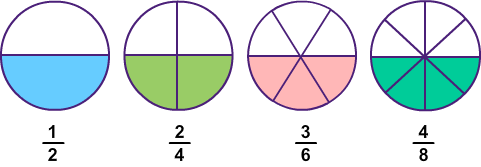
Equivalent fractions are also a significant concept for students to understand. Equivalent fractions are those that represent the same part of a whole but are written differently. For example, 1/2 and 3/6 are equivalent fractions because they both represent half of a whole.
By mastering the skill of comparing fractions, students will be able to solve a broad range of problems involving fractions, such as ordering fractions, adding and subtracting fractions, and solving fraction word problems.
Leave a Reply